Voice is the future. The world’s technology giants are clamoring for vital market share, with ComScore projecting that “50% of all searches will be voice searches by 2020.”
However,
the historical antecedents that have led us to this point are as
essential as they are surprising. Within this report, we take a trip
through the history of speech recognition technology, before providing a
comprehensive overview of the current landscape and the tips that all
marketers need to bear in mind to prepare for the future.
The History of Speech Recognition Technology
Speech
recognition technology entered the public consciousness rather
recently, with the glossy launch events from the tech giants making
worldwide headlines.
The appeal is instinctive; we are fascinated by machines that can understand us.
From
an anthropological standpoint, we developed the spoken word long in
advance of its written counterpart and we can speak 150 words per
minute, compared with the paltry 40 words the average person can type in
60 seconds.
In
fact, communicating with technological devices via voice has become so
popular and natural that we may be justified in wondering why the
world’s richest companies are only bringing these services to us now.
The
history of the technology reveals that speech recognition is far from a
new preoccupation, even if the pace of development has not always
matched the level of interest in the topic. As we can see below, major
breakthroughs dating back to the 18th century have provided the platform
for the digital assistants we all know today.
The
earliest advances in speech recognition focused mainly on the creation
of vowel sounds, as the basis of a system that might also learn to
interpret phonemes (the building blocks of speech) from nearby
interlocutors.
These
inventors were hampered by the technological context in which they
lived, with only basic means at their disposal to invent a talking
machine. Nonetheless, they provide important background to more recent
innovations.
Dictation
machines, pioneered by Thomas Edison in the late 19th century, were
capable of recording speech and grew in popularity among doctors and
secretaries with a lot of notes to take on a daily basis.
However,
it was not until the 1950s that this line of inquiry would lead to
genuine speech recognition. Up to this point, we see attempts at speech
creation and recording, but not yet interpretation.
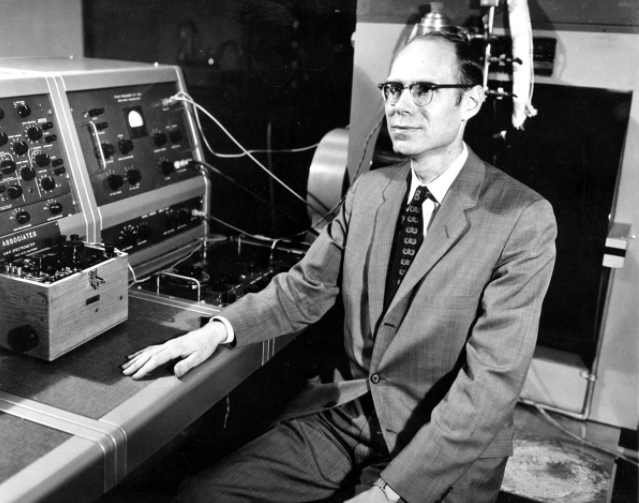
Audrey,
a machine created by Bell Labs, could understand the digits 0–9, with a
90% accuracy rate. Interestingly, this accuracy level was only recorded
when its inventor spoke; it hovered between 70% and 80% when other
people spoke to Audrey.

This
hints at some of the persistent challenges of speech recognition; each
individual has a different voice and spoken language can be very
inconsistent. Unlike text, which has a much greater level of
standardization, the spoken word varies greatly based on regional
dialects, speed, emphasis, even social class and gender. Therefore,
scaling any speech recognition system has always been a significant
obstacle.
Alexander
Waibel, who worked on Harpy, a machine developed at Carnegie Mellon
University that could understand over 1,000 words, built on this point:
“So you have things like ‘euthanasia’, which could be ‘youth in Asia’. Or if you say ‘Give me a new display’ it could be understood as ‘give me a nudist play’.”
Until
the 1990s, even the most successful systems were based on template
matching, where sound waves would be translated into a set of numbers
and stored. These would then be triggered when an identical sound was
spoken into the machine. Of course, this meant that one would have to
speak very clearly, slowly, and in an environment with no background
noise to have a good chance of the sounds being recognized.
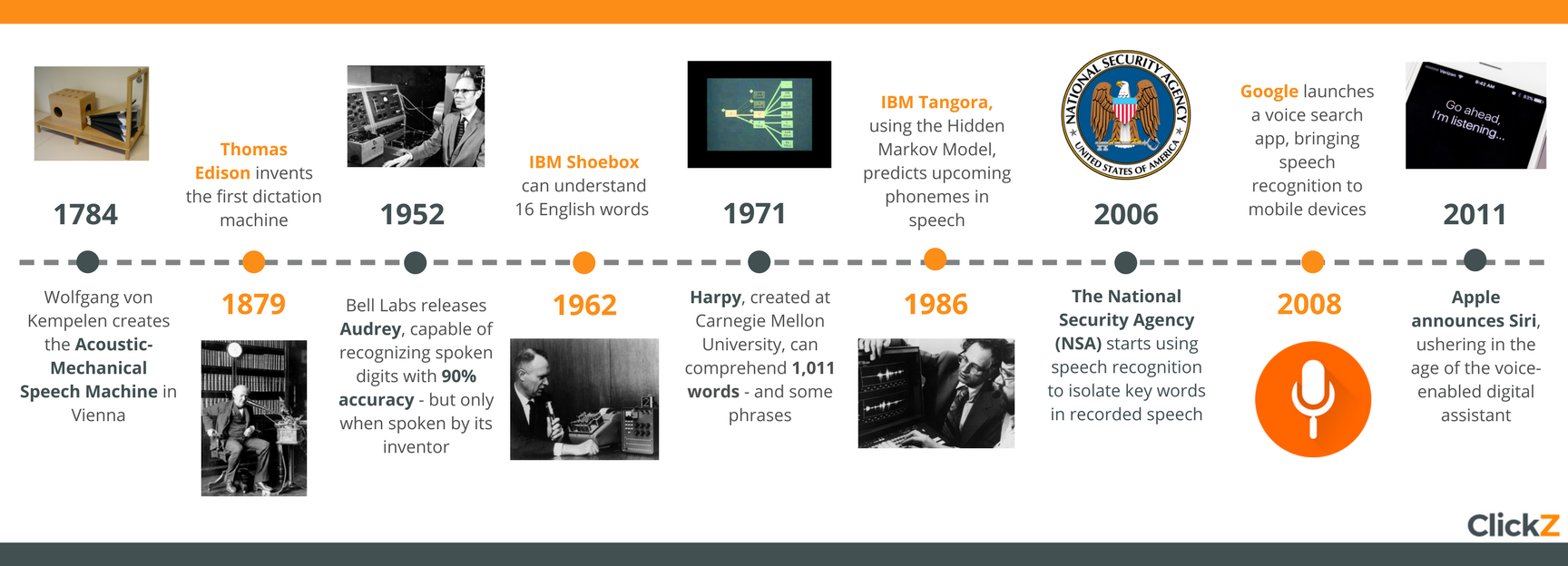
IBM
Tangora, released in the mid-1980s and named after Albert Tangora, then
the world’s fastest typist, could adjust to the speaker’s voice. It
still required slow, clear speech and no background noise, but its use
of hidden Markov models allowed for increased flexibility through data
clustering and the prediction of upcoming phonemes based on recent
patterns.
Although
it required 20 minutes of training data (in the form of recorded
speech) from each user, Tangora could recognize up to 20,000 English
words and some full sentences.
The
seeds are sown here for voice recognition, one of the most significant
and essential developments in this field. It was a long-established
truism that speech recognition could only succeed by adapting to each
person’s unique way of communicating, but arriving at this breakthrough
has been much easier said than done.
It
was only in 1997 that the world’s first “continuous speech recognizer”
(ie. one no longer had to pause between each word) was released, in the
form of Dragon’s NaturallySpeaking software. Capable of understanding
100 words per minute, it is still in use today (albeit in an upgraded
form) and is favored by doctors for notation purposes.
Machine
learning, as in so many fields of scientific discovery, has provided
the majority of speech recognition breakthroughs in this century. Google
combined the latest technology with the power of cloud-based computing
to share data and improve the accuracy of machine learning algorithms.
This culminated in the launch of the Google Voice Search app for iPhone in 2008.
Driven
by huge volumes of training data, the Voice Search app showed
remarkable improvements on the accuracy levels of previous speech
recognition technologies. Google built on this to introduce elements of
personalization into its voice search results, and used this data to
develop its Hummingbird algorithm, arriving at a much more nuanced
understanding of language in use. These strands have been tied together
in the Google Assistant, which is now resident on almost 50% of all
smartphones.
It
was Siri, Apple’s entry into the voice recognition market, that first
captured the public’s imagination, however. As the result of decades of
research, this AI-powered digital assistant brought a touch of humanity
to the sterile world of speech recognition.

After
Siri, Microsoft launched Cortana, Amazon launched Alexa, and the wheels
were set in motion for the current battle for supremacy among the tech
giants’ respective speech recognition platforms.
In
essence, we have spent hundreds of years teaching machines to complete a
journey that takes the average person just a few years. Starting with
the phoneme and building up to individual words, then to phrases and
finally sentences, machines are now able to understand speech with a
close to 100% accuracy rate.
The
techniques used to make these leaps forward have grown in
sophistication, to the extent that they are now loosely based on the
workings of the human brain. Cloud-based computers have entered millions
of homes and can be controlled by voice, even offering conversational
responses to a wide range of queries.
That journey is still incomplete, but we have travelled quite some distance from the room-sized computers of the 1950s.
The Current Speech Recognition Landscape
Smartphones
were originally the sole place of residence for digital assistants like
Siri and Cortana, but the concept has been decentralized over the past
few years.
At
present, the focus is primarily on voice-activated home speakers, but
this is essentially a Trojan horse strategy. By taking pride of place in
a consumer’s home, these speakers are the gateway to the proliferation
of smart devices that can be categorized under the broad ‘Internet of
Things’ umbrella. A Google Home or Amazon Echo can already be used to
control a vast array of Internet-enabled devices, with plenty more due
to join the list by 2020. These will include smart fridges, headphones,
mirrors, and smoke alarms, along with an increased list of third-party
integrations.
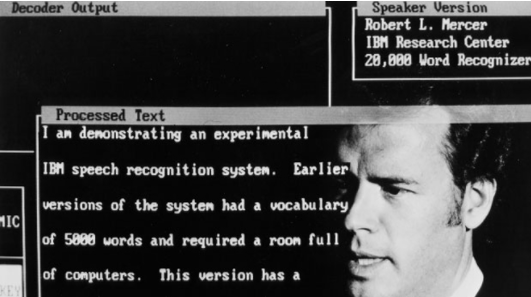
Recent Google research
found that over 50% of users keep their voice-activated speaker in
their living room, with a sizeable number also reporting that they have
one in their bedroom or kitchen.
And
this is exactly the point; Google (and its competitors) want us to buy
more than one of these home devices. The more prominent they are, the
more people will continue to use them.
Their
ambition is helped greatly by the fact that the technology is now
genuinely useful in the accomplishment of daily tasks. Ask Alexa, Siri,
Cortana, or Google what the weather will be like tomorrow and it will
provide a handy, spoken summary. It is still imperfect, but speech
recognition has reached an acceptable level of accuracy for most people
now, with all major platforms reporting an error rate of under 5%.
As
a result, these companies are at pains to plant their flag in our homes
as early as possible. Hardware, for example in the shape of a home
speaker system, is not something most of us purchase often. For example,
if a consumer buys a Google Home, it seems probable that they will
complement this with further Google-enabled devices, rather than
purchase from a rival company and create a disjointed digital ecosystem
under their roof. Much easier to seek out devices that will enable
continuity and greater convenience.
For this reason, it makes sense for Amazon to sell the Echo Dot for as low as $29.99. That equates to a short-term financial loss for Amazon on each device sold, but the long-term gains will more than make up for it.
There are estimated to be 33 million smart speakers in circulation already (Voice Labs report, 2017) and both younger and older generations are adopting the technology at a rapid rate.
Tech Crunch reports that,
In fact, the demographics of an assistant “superuser,” someone who spends twice the amount of time with personal assistants on a monthly basis than average — is a 52-year old woman, spending 1.5 hours per month with assistant apps.
Perhaps
most importantly for the major tech companies, consumers are
increasingly comfortable making purchases through their voice-enabled
devices.
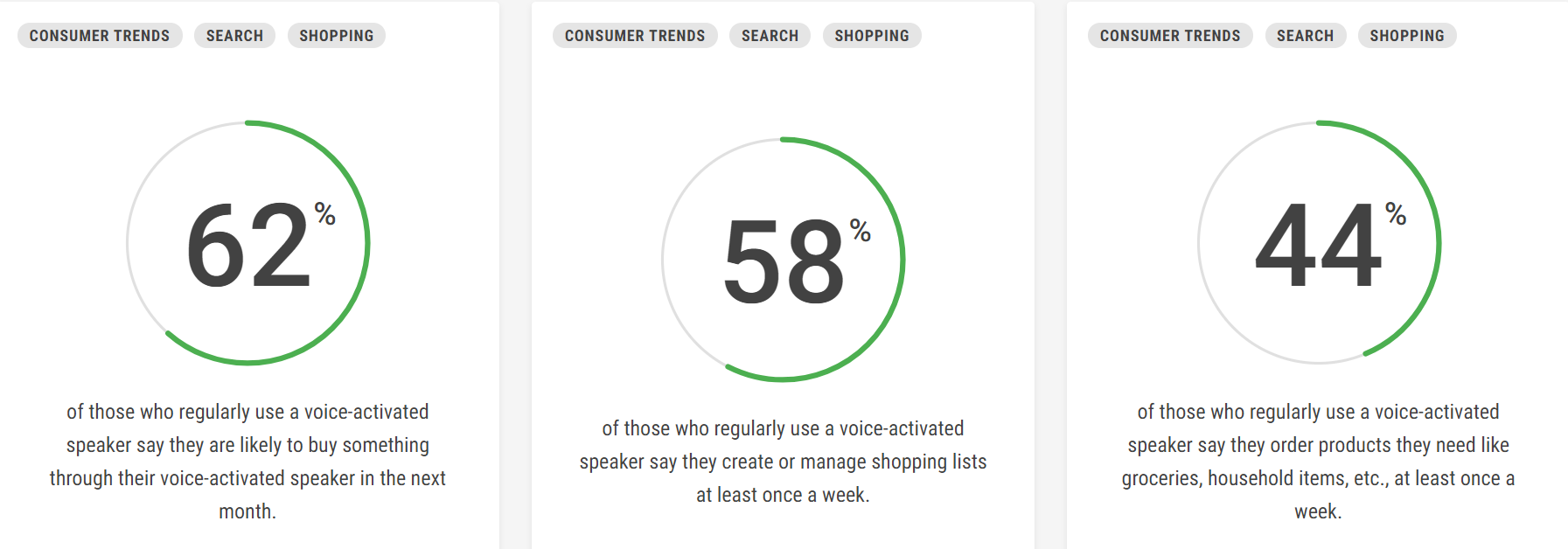
Google
reports that 62% of users plan to make a purchase through their speaker
over the coming month, while 58% use theirs to create a weekly shopping
list:
Short-term
conclusions about the respective business strategies of Amazon and
Google, in particular, are relatively easy to draw. The first-mover
advantage looks set to be marked in this arena, especially as speech
recognition continues to develop into conversational interactions that
lead to purchases.
We have written before
about the two focal points of the voice search strategy for the tech
giants: the technology should be ubiquitous and it must be seamless.
Voice is already a multi-platform ecosystem, but we are some distance
from the ubiquity it seeks.
To
gain insight into the likely outcome of the current competition, it is
worth assessing the strengths and weaknesses of the four key players in
western markets: Amazon, Google, Apple, and Microsoft.

Amazon
First-party Hardware: Echo, Echo Dot, Echo Show, Fire TV Stick, Kindle.
Digital Assistant: Alexa
Usage Statistics:
- “Tens of millions of Alexa-enabled devices” sold worldwide over the 2017 holiday season (Amazon)
- 75% of all smart speakers sold to date are Amazon devices (Tech Republic)
- The Echo Dot was the number one selling device on Amazon over the holidays, with the Alexa-enabled Fire TV stick in second place. (Amazon)
- The average Alexa user spends 18 minutes a month interacting with the device, compared to just five minutes for Google Home (Gartner)
- There are now over 25,000 skills available for Alexa (Amazon)
Overview:
The
cylindrical Echo device and its younger sibling, the Echo Dot, have
been the runaway hit of the smart speaker boom. By tethering the
speakers to a range of popular third-party services and ‘skills’, Amazon
has succeeded in making the Echo a useful addition to millions of
households.
As Dave Limp, head of Amazon devices, put it recently,
“We think of it as ambient computing, which is computer access that’s less dedicated personally to you but more ubiquitous.”
Ubiquity seems a genuine possibility, based on the sales figures.
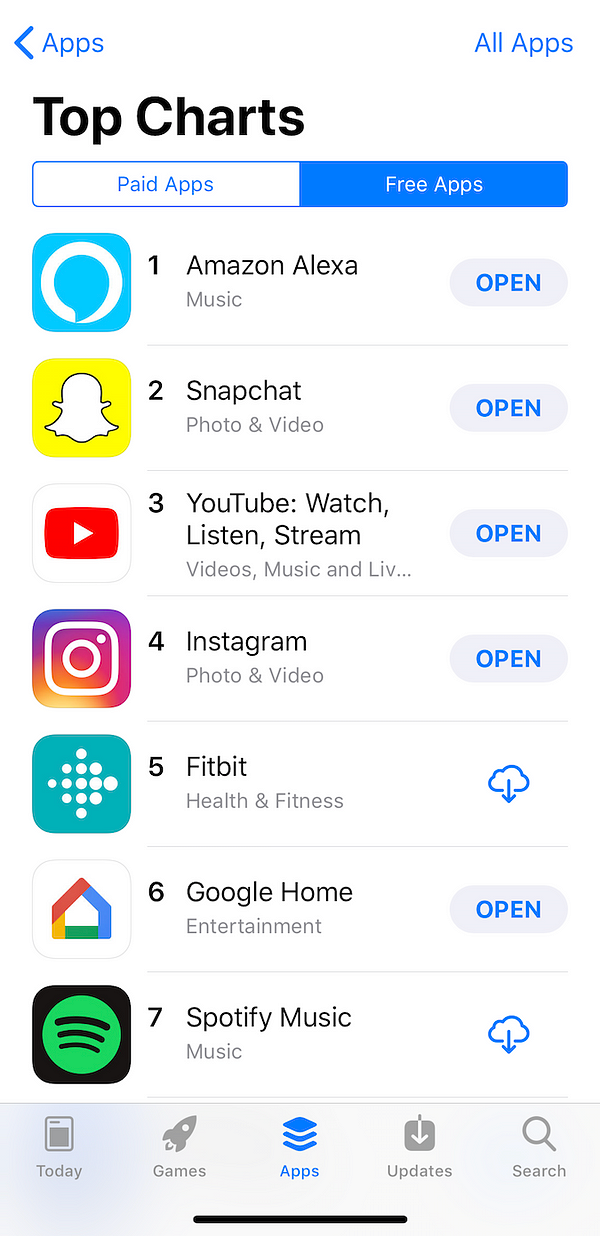
After
a holiday season when the Echo Dot became the most popular product on
Amazon worldwide, the Alexa app occupied top position in the App Store,
ahead of Google’s rival product.
Amazon’s
heritage as an online retailer gives it an innate advantage when it
comes to monetizing the technology, too. The Whole Foods acquisition
adds further weight to this, with the potential to integrate the offline
and online worlds in a manner other companies will surely envy.
Moreover,
Amazon has never depended on advertising to keep its stock prices
soaring. Quite the contrary, in fact. As such, there is less short-term
pressure to force this aspect of their smart speakers.
With
advertisers keen to find a genuine online alternative to Google and
Facebook, Amazon is in a great position to capitalize. There is a fine
balancing act to maintain here, nonetheless. Amazon has most to lose, in
terms of consumer trust and reputation, so it will only move into
advertising for Alexa carefully.
The company denies it has plans to do so, but as research company L2 Inc wrote recently,
Amazon has approached major brands asking if they would be willing to pay for Amazon’s Choice, a designation given to best-in-class products in a particular category.
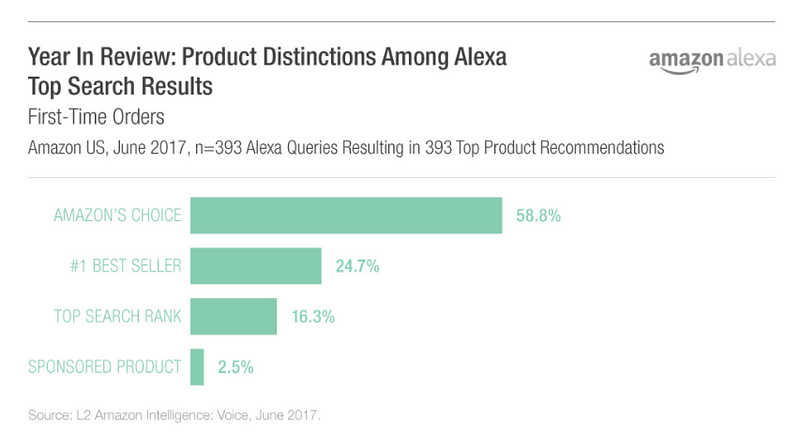
We
should expect to see more attempts from Amazon to provide something
beyond just paid ads on search results. Voice requires new advertising
solutions and Amazon will tread lightly at first to ensure it does not
disrupt the Alexa experience. The recently announced partnership with publishing giant Hearst is a sign of things to come.
The
keys to Alexa’s success will be the integration of Amazon’s own assets,
along with the third-party support that has already led to the creation
of over 25,000 skills. With support announced
for new headphones, watches, fridges, and more, Amazon looks set to
stay at the forefront of voice recognition technology for some time to
come.

First-party Hardware: Google Home, Google Home Mini, Google Home Max, Pixelbook, Pixel smartphones, Pixel Buds, Chromecast, Nest smart home products.
Digital Assistant: Google Assistant
Usage Statistics:
- Google Home has a 24% share of the US smart speaker market (eMarketer)
- There are now over 1,000 Actions for Google Home (Google)
- Google Assistant is available on over 225 home control brands and more than 1,500 devices (Google)
- The most popular Google Assistant apps are games, followed closely by home control applications (Voicebot.ai)

Overview:
Google
Assistant is directly tied to the world’s biggest search engine,
providing users with direct access to the largest database of
information ever known to mankind. That’s not a bad repository for a
digital assistant to work with, especially as Google continues to make
incremental improvements to its speech recognition software.
Recent
research from Stone Temple Consulting across 5,000 sample queries found
Google to be the most accurate solution, by quite some distance:
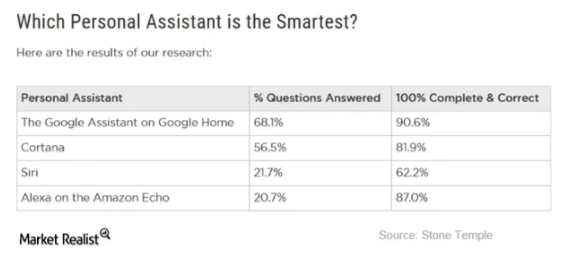
Combined
with Google Photos, Google Maps, YouTube, and a range of other
effective services, Google Assistant has no shortage of integration
possibilities.
Google
may not have planned to enter the hardware market again after the
lukewarm reception for its products in the past. However, this new
landscape has urged the search giant into action in a very serious way.
There is no room for error at the moment, so Google has taken matters
into its own hands with the Pixel smartphones, the Chromecast, and of
course the Home devices.
The
Home Mini has been very popular, and Google has added the Home Max to
the collection, which comes in at a higher price than even the Apple
HomePod. All bases are very much covered.
Google
knows that the hardware play is not a long-term solution. It is a
necessary strategy for the here and now, but Google will want to
convince other hardware producers to integrate the Assistant, much in
the same way it did with Android smartphone software. That removes the
expensive production costs but keeps the vital currency of consumer
attention spans.
This plan is already in action, with support just announced for a range of smart displays:
This
adds a new, visual element to consumer interactions with smart speakers
and, vitally, brings the potential to use Google Photos, Hangouts, and
YouTube.
Google also wants to add a “more human touch” to its AI assistant and has hired a team of comedians, video game designers, and empathy experts to inject some personality.
Google
is, after all, an advertising company, so the next project will be to
monetize this technology. For now, the core aim is to provide a better,
more human experience than the competition and gain essential territory
in more households. The search giant will undoubtedly find novel ways to
make money from that situation.
Although
it was slower off the mark than Amazon, Google’s advertising nous and
growing range of products mean it is still a serious contender in both
the short- and long-term.

Apple
Hardware: Apple HomePod (Due to launch in 2018 at $349), iPhone, MacBooks, AirPods
Digital Assistant: Siri
Usage Statistics:
- 42.5% of smartphones have Apple’s Siri digital assistant installed (Highervisibility)
- 41.4 million monthly active users in the U.S. as of July 2017, down 15% on the previous year (Verto Analytics)
- 19% of iPhone users engage with Siri at least daily (HubSpot)
Overview:
Apple
retains an enviable position in the smartphone and laptop markets,
which has allowed it to integrate Siri with its OS in a manner that
other companies simply cannot replicate. Even Samsung, with its Bixby
assistant, cannot boast this level of synergy, as its smartphones
operate on Android and, as a result, have to compete with Google
Assistant for attention.
Nonetheless,
it is a little behind the curve when it comes to getting its hardware
into consumers’ home lives. The HomePod will, almost certainly, deliver a
much better audio experience than the Echo Dot or Google Home Mini,
with a $350 price tag to match. It will contain a host of impressive
features, including the ability to judge the surrounding space and
adjust the sound quality accordingly.

The
HomePod launch has been delayed, with industry insiders suggesting that
Siri is the cause. Apple’s walled garden approach to data has its
benefits for consumers, but it has its drawbacks when it comes to
technologies like voice recognition. Google has access to vast
quantities of information, which it processes in the cloud and uses to
improve the Assistant experience for all users. Apple does not possess
this valuable resource in anything like the same quantity, which has
slowed the development of Siri since its rise to fame.
That said, these seem likely to be short-term concerns.
Apple
will stay true to its core business strategy and it is one that is
served it rather well so far. The HomePod will sit at the premium end of
the market and will lean on Apple’s design heritage, with a focus on
providing a superior audio experience. It will launch with support for
Apple Music alone, so unless Apple opens up its approach to third
parties, it could be one for Apple fans only. Fortunately for Apple,
there are enough of those to ensure the product gains a foothold.
Whether its

Microsoft
Hardware: Harman/kardon Invoke speaker, Windows smartphones, Microsoft laptops
Digital Assistant: Cortana
Usage Statistics:
- 5.1% of smartphones have the Cortana assistant installed
- Cortana now has 133 million monthly users (Tech Radar)
- 25% of Bing searches are by voice (Microsoft)
Overview:
Microsoft
has been comparatively quiet on the speech recognition front, but it
possesses many of the component parts required for a successful speech
recognition product.
With
a very significant share of the business market, the Office suite of
services, and popular products like Skype and LinkedIn, Microsoft
shouldn’t be written off.

Apple’s
decision to default to Google results over Bing on its Siri assistant
was a blow to Microsoft’s ambitions, but Bing can still be a competitive
advantage for Microsoft in this arena. Bing is a source of invaluable
data and has helped develop Cortana into a much more effective speech
recognition tool.
The Invoke speaker, developed by Harman/kardon with Cortana integrated into the product, has also been reduced to a more approachable $99.95.
There
are new Cortana-enabled speakers on the way, along with smart home
products like thermostats. This should see its levels of uptake
increase, but the persistent feeling is that Microsoft may be a little
late to this party already.
Where
Microsoft can compete very credibly is in the office environment, which
has also become a central consideration for Amazon. Microsoft is
prepared to take a different route to gain a foothold in this market,
but it could still be a very profitable one.
The Future of Speech Recognition Technology
We
are still some distance from realizing the true potential of speech
recognition technology. This applies both to the sophistication of the
technology itself and to its integration into our lives. The current
digital assistants can interpret speech very well, but they are not the
conversational interfaces that the technology providers want them to be.
Moreover, speech recognition remains limited to a small number of
products.
The rate of progress, compared to the earliest forays into speech recognition, is really quite phenomenal nonetheless.
As
such, we can look into the near future and envisage a vastly changed
way of interacting with the world around us. Amazon’s concept of
“ambient computing” seems quite fitting.
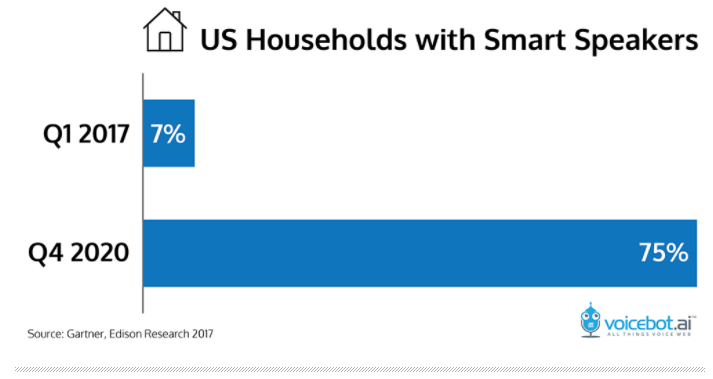
The
smart speaker market has significant room left to grow, with 75% of US
homes projected to have at least one by the end of 2020.
Now
that users are getting over the initial awkwardness of speaking to
their devices, the idea of telling Alexa to boil the kettle or make an
espresso does not seem so alien.
Voice is becoming an interface of its own, moving beyond the smartphone to the home and soon, to many other quotidian contexts.
We
should expect to see more complex input-output relationships as the
technology advances, too. Voice-voice relationships restrict the
potential of the response, but innovations like the Amazon Echo Show and
Google’s support for smart displays will open up a host of new
opportunities for engagement. Apple and Google will also incorporate
their AR and VR applications when the consumer appetite reaches the
required level.
Challenges
remain, however. First of all, voice search providers need to figure
out a way to provide choice through a medium that lends itself best to
short responses. Otherwise, how would it be possible to ensure that a
user is getting the best response to their query, rather than the
response with the highest ad budget behind it?
Modern
consumers are savvy and have access to almost endless information, so
any misjudgements from brands will be documented and shared with the
user’s network.
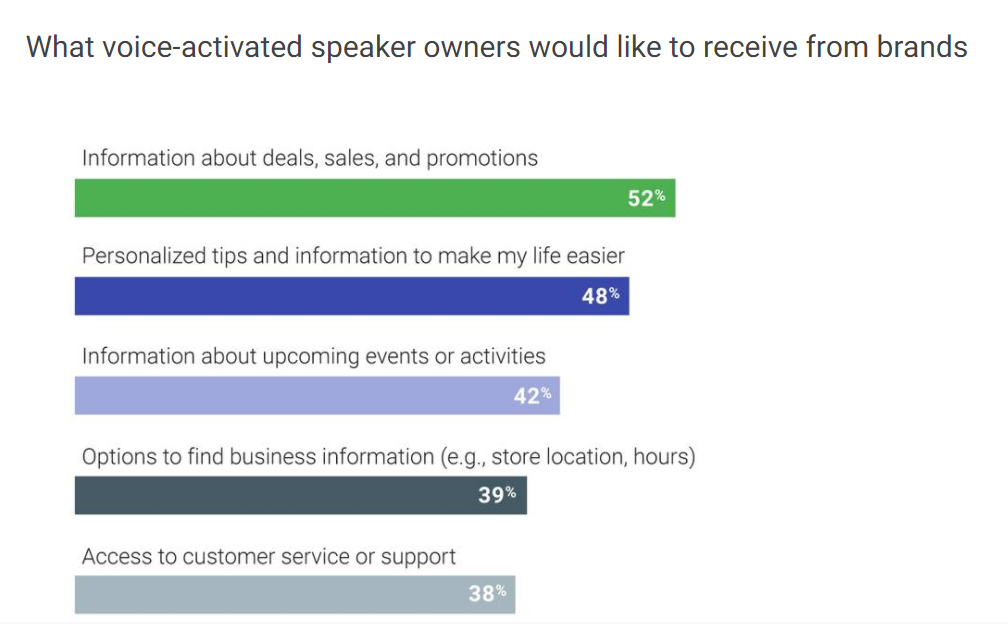
A
new study from Google has shown that there is an increasing acceptance
among consumers that brands will use smart speakers to communicate with
them. A sizeable number revealed a willingness to receive information
about deals and sales, with almost half wanting to receive personalized
tips:
Speech
recognition technology provides the platform for us to communicate
credibly, but it is up to marketers to make the relationship with their
audience mutually beneficial.
Key Takeaways
- Brands need to consider how they can make an interaction more valuable for a consumer. The innate value proposition of voice search is that it is quick, convenient, and helpful. It is only by assimilating with — and adding to -this relationship between technology and consumer that they will cut through. The Beauty and the Beast example provides an early, cautionary tale for all of us.
- Amazon is in prime position to monetize its speech recognition technology, but still faces obstacles. Sponsorship of Amazon’s Choice has been explored as a route to gain revenue without losing customers.
- Google has made speech recognition a central focus for the growth of their business. With a vast quantity of data at its disposal and increasing third-party support, Google Assistant will provide a serious threat to Amazon’s Alexa this year.
- Marketers should take advantage of technical best practices for voice search to increase visibility today. While this technology is still developing, we need to give it a helping hand as it completes its mammoth tasks.
- The best way to understand how people use speech recognition technology is to engage with it frequently. Marketers serious about pinpointing areas of opportunity should be conducting their own research at home, at work, and on the go.

No comments:
Write comments